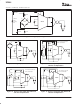
Datasheet
"#$#
SBOS146A − OCTOBER 1986 − REVISED AUGUST 2004
www.ti.com
12
ESTABLISHING R
S
:
The input full-scale span is 58mV (∆e
INFS
= 58mV).
R
S
is found from Equation 1.
R
S
+
40
DI
O
ńDe
IN
* 0.016
amps
volt
+
40
16mAń58mV * 0.016AńV
+
40
0.2599
+ 153.9W
SELECTING R
4
:
R
4
is chosen to make the output 4mA at T
TC
= 0°C
(V
TC
= −1.28mV) and T
D
= +25°C (V
D
= 0.6V); see
Figure 10.
V
TC
will be −1.28mV when T
TC
= 0°C and the reference
junction is at +25°C. e
1
must be computed for the condition
of T
D
= +25°C to make e
IN
= 0V.
V
D25
o
C
+ 600mV
e
125
o
C
+ 600mV
ǒ
51
2051
Ǔ
+ 14.9mV
e
IN
+ e
2
* e
1
+ V
TC
) V
4
* e
1
With e
IN
= 0 and V
TC
= −1.28mV,
V
4
+ e
1
) e
IN
* V
TC
+ 14.9mV ) 0V *
(
* 1.28mV
)
1mA
(
R
4
)
+ 16.18mV
R
4
+ 16.18W
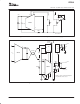
COLD JUNCTION COMPENSATION:
A temperature reference circuit is shown in Figure 11.
The diode voltage has the form:
V
D
+
KT
q
ln
I
DIODE
I
SAT
Typically at T
2
= +25°C, V
D
= 0.6V and ∆V
D
/∆T = −2mV/°C.
R
5
and R
6
form a voltage divider for the diode voltage V
D
.
The divider values are selected so that the gradient
∆V
D
/∆T equals the gradient of the thermocouple at the
reference temperature. At +25°C this is approximately
52µV/°C (obtained from a standard thermocouple table);
therefore,
DT
C
DT
+
DV
D
DT
ǒ
R
6
R
5
) R
6
Ǔ
52mV
C
+
2000mV
C
ǒ
R
6
R
5
) R
6
Ǔ
°°
R
5
is chosen as 2kΩ to be much larger than the resistance
of the diode. Solving for R
6
yields 51Ω.
V
5
1mA
R
5
+
−
V
6
R
6
+
−
V
D
+
−
D
Figure 11. Cold Junction Compensation Circuit
THERMOCOUPLE BURN-OUT INDICATION
In process control applications it is desirable to detect
when a thermocouple has burned out. This is typically
done by forcing the two-wire transmitter current to either
limit when the thermocouple impedance goes very high.
The circuits of Figure 16 and Figure 17 inherently have
downscale indication. When the impedance of the
thermocouple gets very large (open) the bias current
flowing into the + input (large impedance) will cause I
O
to
go to its lower range limit value (about 3.8mA). If upscale
indication is desired, the circuit of Figure 18 should be
used. When T
C
opens, the output will go to its upper range
limit value (about 25mA or higher).
OPTIONAL INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE TRIM
The XTR101 has provisions for nulling the input offset
voltage associated with the input amplifiers. In many
applications the already low offset voltages (30µV max for
the B grade and 60µV max for the A grade) will not need
to be nulled at all. The null adjustment can be done with a
potentiometer at pins 1, 2, and 14; see Figure 5 and
Figure 6. Either of these two circuits may be used.
NOTE: It is not recommended to use this input offset
voltage nulling capability for elevation or suppression. See
the Signal Suppression and Elevation section for the
proper techniques.
(2)