Datasheet
®
3
PCM1725
PIN ASSIGNMENTS
PIN NAME I/O FUNCTION
1
(1)
LRCIN IN Sample Rate Clock Input
2
(1)
DIN IN Audio Data Input
3
(1)
BCKIN IN Bit Clock Input for Audio Data.
4 NC — No Connection
5 CAP — Common Pin of Analog Output Amp
6V
OUT
R OUT Right-Channel Analog Output
7 GND — Ground
8V
CC
— Power Supply
9V
OUT
L OUT Left-Channel Analog Output
10 NC — No Connection
11 NC — No Connection
12
(2)
DM IN De-emphasis Control
HIGH: De-emphasis ON
LOW: De-emphasis OFF
13
(2)
FORMAT — Audio Data Format Select
HIGH: I
2
S Data Format
LOW: Standard Data Format
14 SCKI IN System Clock Input (256f
S
or 384f
S
)
NOTES: (1) Schmitt Trigger input. (2) Schmitt Trigger input with internal
pull-up.
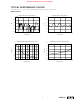
PIN CONFIGURATION
TOP VIEW SOIC
LRCIN
DIN
BCKIN
NC
CAP
V
OUT
R
GND
SCKI
FORMAT
DM
NC
NC
V
OUT
L
V
CC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
PCM1725
PACKAGE INFORMATION
PACKAGE DRAWING
PRODUCT PACKAGE NUMBER
(1)
PCM1725U 14 Pin SOIC 235
NOTE: (1) For detailed drawing and dimension table, please see end of data
sheet, or Appendix C of Burr-Brown IC Data Book.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Power Supply Voltage ....................................................................... +6.5V
+V
CC
to +V
DD
Difference ................................................................... ±0.1V
Input Logic Voltage .................................................. –0.3V to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
Power Dissipation .......................................................................... 290mW
Operating Temperature Range ......................................... –25°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature ...................................................... –55°C to +125°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 5s) .................................................. +260°C
Thermal Resistance,
θ
JA
.............................................................. +90°C/W
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Burr-Brown
recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling
and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation
to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may
be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric
changes could cause the device not to meet its published
specifications.
Not Recommended For New Designs