Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- FEATURES
- APPLICATIONS
- DESCRIPTION
- DESCRIPTION (Continued)
- POWER DISSIPATION RATINGS
- ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
- RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
- DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- DRIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
- RECEIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- RECEIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
- DEVICE SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
- PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
- DEVICE INFORMATION
- FUNCTION TABLES
- TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- APPLICATION INFORMATION
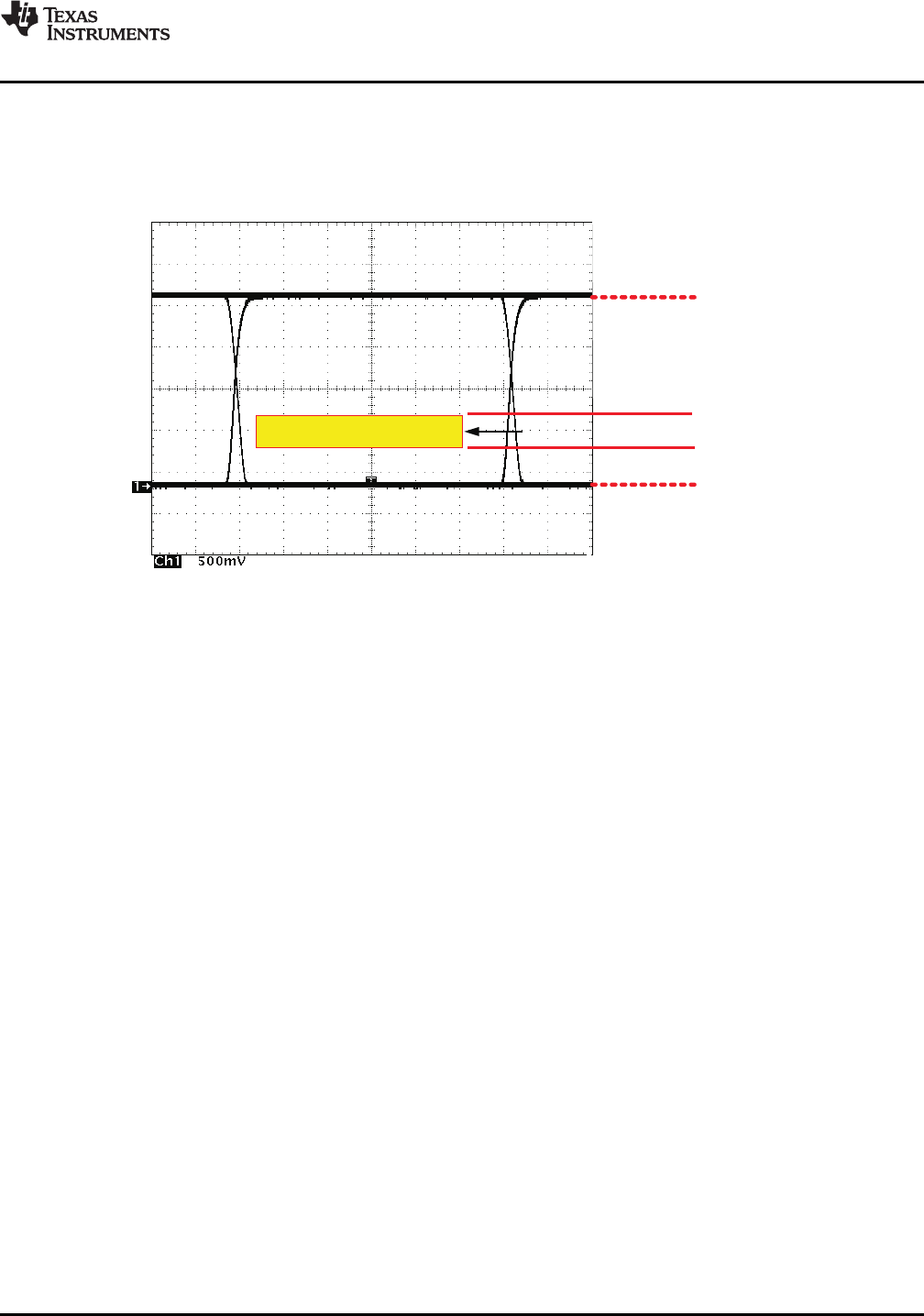
Differential Signal
75% SAMPLEPOINT
500 mVThreshold
900 mVThreshold
NOISEMARGIN
NOISEMARGIN
RECEIVERDETECTIONWINDOW
Interoperability of 3.3-V CAN in 5-V CAN Systems
SN65HVD233
SN65HVD234
SN65HVD235
www.ti.com
.............................................................................................................................................. SLLS557F – NOVEMBER 2002 – REVISED AUGUST 2008
CAN is a differential bus where complementary signals are sent over two wires and the voltage difference
between the two wires defines the logical state of the bus. The differential CAN receiver monitors this voltage
difference and outputs the bus state with a single-ended output signal.
Figure 29. Typical SN65HVD230 Differential Output Voltage Waveform
The CAN driver creates the difference voltage between CANH and CANL in the dominant state. The dominant
differential output of the SN65HVD230 is greater than 1.5 V and less than 3 V across a 60-ohm load. The
minimum required by ISO 11898 is 1.5 V and maximum is 3 V. These are the same limiting values for 5 V
supplied CAN transceivers. The bus termination resistors drive the recessive bus state and not the CAN driver.
A CAN receiver is required to output a recessive state with less than 500 mV and a dominant state with more
than 900 mV difference voltage on its bus inputs. The CAN receiver must do this with common-mode input
voltages from -2 V to 7 volts. The SN65HVD230 family receivers meet these same input specifications as 5-V
supplied receivers.
Common-Mode Signal
A common-mode signal is an average voltage of the two signal wires that the differential receiver rejects. The
common-mode signal comes from the CAN driver, ground noise, and coupled bus noise. Obviously, the supply
voltage of the CAN transceiver has nothing to do with noise. The SN65HVD230 family driver lowers the
common-mode output in a dominant bit by a couple hundred millivolts from that of most 5-V drivers. While this
does not fully comply with ISO 11898, this small variation in the driver common-mode output is rejected by
differential receivers and does not effect data, signal noise margins or error rates.
The 3.3-V supplied SN65HVD23x family of CAN transceivers are electrically interchangeable with 5-V CAN
transceivers. The differential output is the same. The recessive common-mode output is the same. The dominant
common-mode output voltage is a couple hundred millivolts lower than 5-V supplied drivers, while the receivers
exhibit identical specifications as 5-V devices.
Electrical interoperability does not assure interchangeability however. Most implementers of CAN buses
recognize that ISO 11898 does not sufficiently specify the electrical layer and that strict standard compliance
alone does not ensure interchangeability. This comes only with thorough equipment testing.
Copyright © 2002 – 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 21
Product Folder Link(s): SN65HVD233 SN65HVD234 SN65HVD235