Datasheet
LM1084
www.ti.com
SNVS037F –SEPTEMBER 1999–REVISED MARCH 2013
THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
ICs heats up when in operation, and power consumption is one factor in how hot it gets. The other factor is how
well the heat is dissipated. Heat dissipation is predictable by knowing the thermal resistance between the IC and
ambient (θ
JA
). Thermal resistance has units of temperature per power (C/W). The higher the thermal resistance,
the hotter the IC.
The LM1084 specifies the thermal resistance for each package as junction to case (θ
JC
). In order to get the total
resistance to ambient (θ
JA
), two other thermal resistance must be added, one for case to heat-sink (θ
CH
) and one
for heatsink to ambient (θ
HA
). The junction temperature can be predicted as follows:
T
J
= T
A
+ P
D
(θ
JC
+ θ
CH
+ θ
HA
) = T
A
+ P
D
θ
JA
T
J
is junction temperature, T
A
is ambient temperature, and P
D
is the power consumption of the device. Device
power consumption is calculated as follows:
I
IN
= I
L
+ I
G
P
D
= (V
IN
−V
OUT
) I
L
+ V
IN
I
G
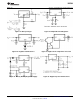
Figure 21 shows the voltages and currents which are present in the circuit.
Figure 21. Power Dissipation Diagram
Once the devices power is determined, the maximum allowable (θ
JA (max)
) is calculated as:
θ
JA (max)
= T
R(max)
/P
D
= T
J(max)
− T
A(max)
/P
D
The LM1084 has different temperature specifications for two different sections of the IC: the control section and
the output section. The Electrical Characteristics table shows the junction to case thermal resistances for each of
these sections, while the maximum junction temperatures (T
J(max)
) for each section is listed in the Absolute
Maximum Ratings section of the datasheet. T
J(max)
is 125°C for the control section, while T
J(max)
is 150°C for the
output section.
θ
JA (max)
should be calculated separately for each section as follows:
θ
JA
(max, CONTROL SECTION) = (125°C - T
A(max)
)/P
D
θ
JA
(max, OUTPUT SECTION) = (150°C - T
A(max)
)/P
D
The required heat sink is determined by calculating its required thermal resistance (θ
HA (max)
).
θ
HA (max)
= θ
JA (max)
− (θ
JC
+ θ
CH
)
(θ
HA (max)
) should also be calculated twice as follows:
(θ
HA (max)
) = θ
JA
(max, CONTROL SECTION) - (θ
JC
(CONTROL SECTION) + θ
CH
)
(θ
HA (max)
) = θ
JA
(max, OUTPUT SECTION) - (θ
JC
(OUTPUT SECTION) + θ
CH
)
If thermal compound is used, θ
CH
can be estimated at 0.2 C/W. If the case is soldered to the heat sink, then a
θ
CH
can be estimated as 0 C/W.
After, θ
HA (max)
is calculated for each section, choose the lower of the two θ
HA (max)
values to determine the
appropriate heat sink.
If PC board copper is going to be used as a heat sink, then Figure 22 can be used to determine the appropriate
area (size) of copper foil required.
Copyright © 1999–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback 11
Product Folder Links: LM1084